Power reliability is a critical factor in maintaining the efficiency and uptime of data centers. Any disruption can lead to costly downtime, data loss, and reputational damage. With the increasing demand for cloud computing, AI, and high-performance computing, ensuring continuous electrical power is more important than ever. Data centers must implement robust power management strategies to prevent outages and maintain operational stability.
Downtime represents the most significant financial risk to data centers due to its direct impact on revenue and operational costs. When a data center experiences an outage, the immediate consequence is the interruption of services, which can lead to substantial financial losses for both the data center’s ownership as well as its client businesses. Even a brief period of downtime can result in lost transactions, decreased productivity, and unsatisfied customers. The financial repercussions for hyperscale data centers and colocation providers extend beyond immediate losses, as these companies may face penalties for failing to meet service level agreements (SLAs); as well as incur additional costs to restore services and address the root causes of the outage. Moreover, the ripple effect of downtime affects supply chains and partner networks … thus amplifying the financial strain across multiple business segments.
Beyond the immediate financial impact, downtime can severely damage a data center’s reputation, leading to long-term financial consequences for the enterprise data center owner and the data center’s public / private investors. This loss of confidence and trust can result in decreased customer retention, hinder the acquisition of new clients, and affect the data center’s market position and revenue streams.
In a competitive landscape where reliability is paramount, the financial risks associated with downtime underscore the critical need for robust power management and contingency planning to safeguard against disruptions and maintain operational excellence. The remainder of this article details the 4 best methods to ensure power reliability in data centers.
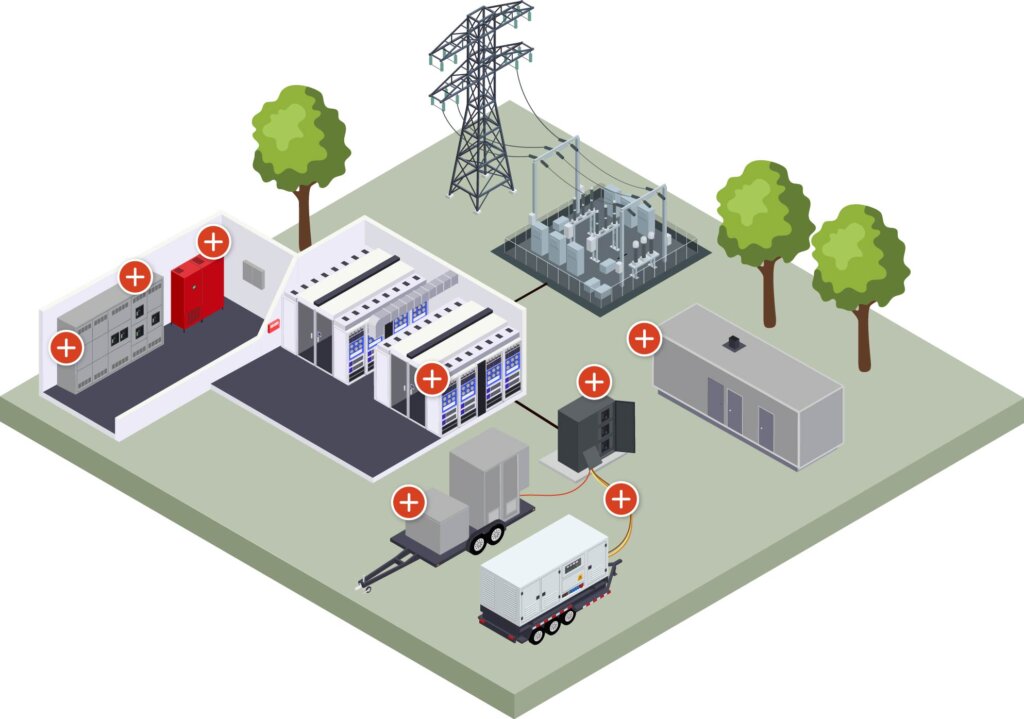
Graphic representation highlighting Trystar’s Data Center Solutions
1. Backup Power Systems
Backup power systems are essential components of a data center’s infrastructure, designed to ensure continuous operation during power disruptions. These systems provide the necessary support to maintain uptime and protect sensitive equipment from power fluctuations.
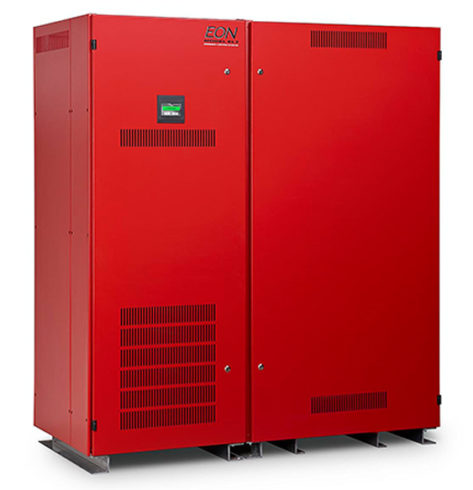

Trystar’s Three-Phase “EON” Emergency Lighting Inverter
Three-Phase Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS): A three-phase UPS is a critical component that provides immediate power backup in the event of a power failure. It ensures a seamless transition by supplying power from its batteries until the primary power source is restored or until generators are online. The three-phase configuration is particularly suited for data centers due to its ability to manage high power loads efficiently, distributing power evenly across the facility and minimizing the risk of overloads.
Three-Phase Emergency Lighting Inverters: These inverters are designed to maintain essential and egress lighting systems during a power outage, ensuring safety and visibility within the data center. By converting DC battery power into AC power, they keep emergency lighting operational, which is crucial for safe evacuation and maintenance activities during a utility power outage. The three-phase design allows for efficient power distribution, supporting large-scale lighting systems typical in data centers.
Generator Docking Stations: A generator docking station is an essential solution for ensuring power reliability … offering a secure, efficient, and compliant connection for both temporary backup generators and load banks used for generator testing. With the increasing frequency of grid instability and extreme weather events, the integration of an automatic transfer switch facilitates seamless power transfer to backup sources, enabling quick restoration of power and enhancing the facility’s resilience against extended power failures. Additionally, this integrated system supports routine generator testing and maintenance within a single, unified unit.
Load Banks: Load banks are used to test and maintain the reliability of backup power systems by simulating the electrical load that a data center would experience during normal operations. By regularly testing generators and UPS systems under load conditions, data centers can ensure that their backup systems are functioning correctly and are ready to manage actual power demands during an outage. This proactive approach helps identify potential issues before they lead to failures, enhancing the overall reliability of the power infrastructure.
2. Power Distribution Redundancy
Power distribution redundancy is a fundamental element of data center design, ensuring continuous power delivery to critical systems even if a component fails. This is achieved by implementing multiple, independent power distribution paths, each capable of supporting the entire power load. Such redundancy allows for seamless operation and immediate power rerouting in case of a fault, maintaining the operational integrity of essential equipment. By using redundant power distribution units and circuit breakers, data centers can isolate and resolve issues without impacting overall performance, thereby enhancing reliability and uptime.
This redundancy also facilitates maintenance and upgrades without disrupting operations, as multiple power paths enable one path to be serviced while others continue to supply power. This flexibility is vital for maintaining infrastructure health and adapting to technological advancements. Additionally, redundant power systems are often equipped with advanced monitoring tools for real-time power usage tracking and quick issue identification. This proactive management not only prevents unexpected outages but also optimizes energy efficiency, contributing to the data center’s sustainability and cost-effectiveness.
3. Real-Time Power Monitoring and Management
Real-time power monitoring and management are essential for maintaining the operational efficiency and reliability of data centers. By continuously tracking power usage and system performance, data centers can quickly identify and address anomalies that could lead to potential failures or inefficiencies. Advanced monitoring systems provide detailed insights into power consumption patterns, enabling data center operators to optimize energy use and reduce operational costs. These systems often include dashboards and alerts that facilitate proactive management, allowing for immediate response to any irregularities. This real-time visibility is crucial for maintaining the delicate balance between performance and energy efficiency, ensuring that data centers operate at peak efficiency while minimizing the risk of downtime.
Sequence of Event Recorders (SERs) and Time Sync Hubs (TSHs) play a pivotal role in enhancing real-time power monitoring and management. Functioning similar to an airplane’s “black box”, Sequence Of Event Recorders are used to log and timestamp events related to power anomalies and equipment performance, providing a chronological record that helps identify the root causes of power disturbances or failures. This detailed event logging … timestamped to the millisecond … is invaluable for data forensics and root cause corrective action (RCCA).
Meanwhile, Time Sync Hubs supply accurate time synchronization for intelligent electronic devices within data centers. TSHs receive time input over an Ethernet network using Precision Time Protocol (PTP) or Network Time Protocol (NTP) to provide accurate time and date information that is essential for time synchronization. TSHs enable data centers to optimize their power management strategies by ensuring that any updates or changes to the power system are based on solid, reliable data.
Together, SERs and TSHs enhance the data center’s ability to maintain continuous, reliable operations through precise monitoring.

4. Regular Testing and Disaster Recovery Planning
Regular testing and disaster recovery planning are crucial for ensuring data center resilience and continuity during unexpected disruptions. Regular testing systematically evaluates critical systems like backup power, network infrastructure, and security protocols to verify their readiness and functionality. This proactive approach identifies vulnerabilities early, allowing for timely corrective actions. By simulating failure conditions, data center personnel can practice response procedures, ensuring preparedness and effective real-world incident response.
Disaster recovery planning complements this by providing a structured framework for quick and efficient recovery from disruptions. It involves developing comprehensive strategies for data backup, restoration, communication, and resource allocation. Clearly defined roles and responsibilities ensure a coordinated response, minimizing downtime and operational impact. Regular reviews and updates of these plans are essential to adapt to technological changes and emerging threats, maintaining data center resilience and service continuity.
Conclusion
Ensuring power reliability in data centers requires a combination of robust power reliability infrastructure, proactive testing and maintenance operations, as well as smart electrical power monitoring. By implementing the 4 best practices noted above, data centers can minimize downtime, enhance efficiency, and protect critical business operations for themselves, their clients, and their investors.
Don’t wait for a power failure to expose vulnerabilities — take action today to strengthen your power reliability strategy and electrical infrastructure!